More than just software: Your team for carbon accounting
We provide personalized support, a TÜV-certified process, and practical online seminars. → Learn more
| August 20, 2025
🕓 Reading time 6 minutes
1. What is CO₂ reporting?
CO₂ reporting refers to the structured calculation, recording, and reporting of a company's greenhouse gas emissions. This is based on international standards such as the GHG Protocol, which ensure that the data collected is comparable and traceable. The aim is to obtain a complete overview of the emissions caused – from a company's own production to supply chains and business travel.
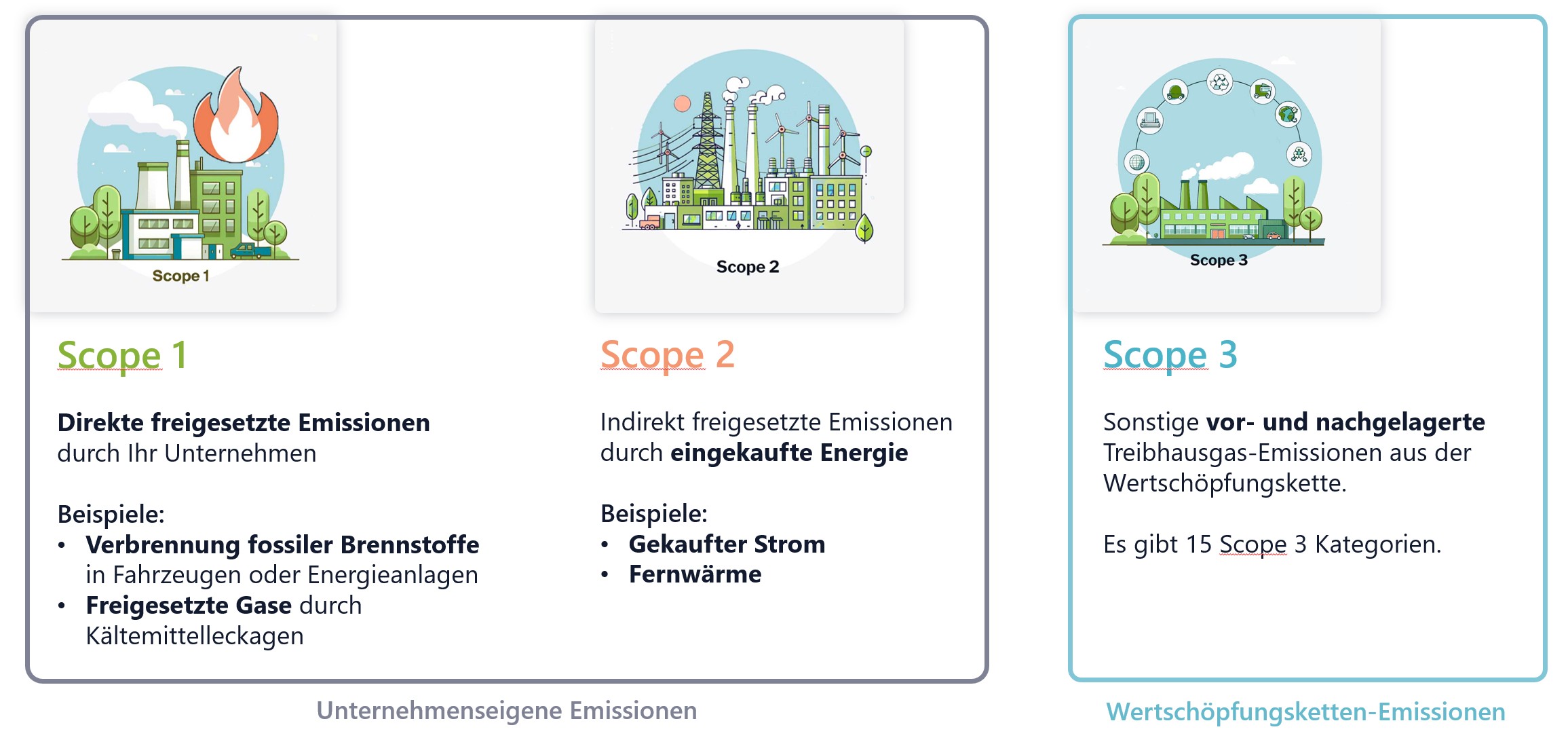
The most common categories are the so-called “scopes”:
-
Scope 1: Direct emissions (e.g., heating systems, company vehicles).
-
Scope 2: Indirect emissions from purchased energy (e.g., electricity, heat).
-
Scope 3: Other indirect emissions along the value chain – from suppliers and business travel to employee mobility.
Complete reporting thus reveals where emission hotspots are located within the company and where there is potential for improvement through targeted measures.

2. Why is CO₂ reporting becoming more relevant for small and medium-sized enterprises?
For many medium-sized companies, CO₂ reporting was not an issue for a long time – but that is changing rapidly. The reasons for this are:
Trickle-down effects and supply chain inquiries
Large companies that are already subject to the CSRD and sustainability reporting are increasingly demanding concrete data on their CO₂ emissions from their suppliers and partners. This also indirectly places an obligation on small and medium-sized enterprises.
CSRD obligation for larger medium-sized companies
Medium-sized companies that exceed the thresholds for employees, total assets, or revenue fall directly within the scope of the CSRD. At that point, at the latest, comprehensive CO₂ reporting across all scopes will become mandatory.
Banks and financing
Credit institutions are paying greater attention to sustainability criteria when granting loans, as they are legally obliged to do so by the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR). Those who can provide transparent information about their emissions receive better terms or access to financing in the first place.
Reputation and competitiveness
Customers, employees, and business partners value credible sustainability and climate-friendly products. Companies that demonstrate where they stand and what measures they are taking through transparent reporting strengthen their brand and competitive position.
A successful start to CO2 management
Stakeholder verstehen und THG-Bilanz praktisch umsetzen
07. Januar 2026, 10.30 bis 11.15 Uhr
3. How does CO₂ reporting work in general?
2. Collect data
All relevant information on Scope 1, 2, and 3 from areas such as energy, purchased goods, business travel, mobility, and operational waste is compiled.
3. Data preparation and calculation of emissions
In the next step, the collected data is processed and converted as necessary in order to calculate the CO₂ emissions using appropriate emission factors.
4. Berichterstattung aufbereiten
The results are summarized in structured reports that can be used for internal purposes as well as for external partners, banks, or customers.
4. How does the CO₂ reporting process work with Green Vision Solutions?
Many medium-sized companies have neither the time nor the specialist expertise to set up CO₂ reporting on their own. This is exactly where we at Green Vision Solutions come in:
1. Informational meeting
In the free initial consultation, you will receive an overview of our TÜV-certified process, which covers all scopes (1, 2, and 3), as well as the software for entering your data. We will also take the time to discuss any questions you may have.
2. Onboarding & project mentor
Each project is supported by an experienced contact person from our family business. You will meet your project mentor at the kick-off meeting. Together, we will clarify the relevant scopes (1, 2, and 3) and categories as well as the raw data required in our input software. Interim consultations and open questions are clarified in an uncomplicated manner at any time.
3. Data collection & calculation
You provide the data – we do the calculations. No special preparatory work is required: whether you need exact supplier data, quantity specifications, costs, or just auxiliary values for statistical projections, we turn it into a complete, auditable corporate carbon footprint.
4. Results & Reporting
The final results will be presented to you in a final meeting. You will also receive a clear dashboard and a report. These can be used directly for reporting or action planning – transparent, comparable, and practical.
Our mission at Green Vision Solutions: To make certified CO₂ reporting as easy as possible for small and medium-sized businesses – understandable, secure, and without unnecessary effort.
Sources
GHG Protocol – GHG Protocol Corporate Standard: https://ghgprotocol.org/corporate-standard Accessed on August 20, 2025
National Grid – What are scope 1, 2 and 3 carbon emissions?: https://www.nationalgrid.com/stories/energy-explained/what-are-scope-1-2-3-carbon-emissions Accessed on August 5, 2025
Environmental Pact Bavaria – The VSME Standard:
https://www.umweltpakt.bayern.de/nachhaltigkeit/fachwissen/420/der-vsme-standard Accessed on April 1, 2025
Coral – The ‘trickle-down’ effect of corporate climate action: https://www.coral.li/blog/the-trickle-down-effect-of-corporate-climate-action Accessed on August 20, 2025
banking.vision – Climate Risks in the Loan Portfolio: Why Reliable Data Matters Now: https://banking.vision/en/climate-risks-financed-emissions/ Accessed on August 20, 2025
Subscribe to our free climate news (de) and never miss any industry news or articles!
Topics
Latest post
Omnibus Regulation: Far-reaching simplifications for the CSRD
Mehr als nur Software: Ihr Team für CO₂-BilanzenWir begleiten mit persönlicher Beratung, einem TÜV-zertifizierten Prozess und praxisnahen...
Introduction to the CO₂ balance
Datensammlung für den Corporate Carbon Footprint: Praxistipps & Erfolgsrezept von Reichold Feinkost
Mehr als nur Software: Ihr Team für CO₂-BilanzenWir begleiten mit persönlicher Beratung, einem TÜV-zertifizierten Prozess und praxisnahen...
Regulatory frameworks
Omnibus Regulation: Far-reaching simplifications for the CSRD
Mehr als nur Software: Ihr Team für CO₂-BilanzenWir begleiten mit persönlicher Beratung, einem TÜV-zertifizierten Prozess und praxisnahen...
Entdecken Sie unsere Seminare & mehr
Find practical training courses on all aspects of greenhouse gas reporting

9.-11.03.26 | 3 Tage | Online
Calculation of the greenhouse gas balance via Scope 1-3
Learn how to calculate GHG emissions yourself - with methods, sources for emission factors and practical relevance

Mi 10.12. | 4 h | Online-Seminar
Materiality analysis and data preparation for CO₂ reporting
Avoid errors and additional effort: Which Scope 1 to 3 data are actually relevant according to GHG?

Do 15.01. | 3 h | Online-Seminar
Scope 3 Data Dilemma
Between data gaps and mountains of data: Coping with GHG in practice




